I Can Explain How Water Will Flow in Different Tonicities
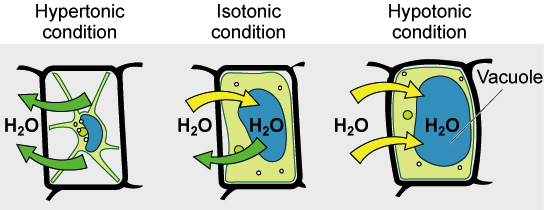
We can use these terms to describe the environment a cell is in. If a cell is in a hypertonic solution the solution has a lower water concentration than the cell cytosol and water moves out of the cell until both solutions are isotonic.
Tonicity Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Solutions Article Khan Academy
When cells are placed in a hypertonic environment higher concentration of solutes than the cell water leaves the cell and the cell becomes shriveled.
. Transcorneal transport ie drug penetration into the eye is not an effective process. Usually there is a higher concentration of solutes on one side of the membrane than the other. Different types of potatoes have varying natural carbohydrate concentrations.
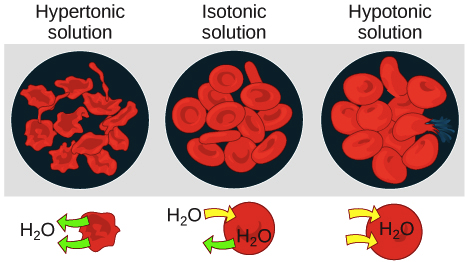
When red blood cells are placed in distilled water which is hypotonic compared to the solution contained within the cells membranes the distilled water will diffuse into the red blood cells and cause them to burst. The cells of our body normally exist in an isotonic environment. Higher concentration of solute.
The flow of water across a membrane in response to differing concentrations of solutes on either side - osmosis - generates a pressure across the membrane called osmotic pressure. Three termshyerptonic hypotonic and isotonicare used to describe whether. Cut four strips of dialysis tubing each 150 cm long.
On the other hand if the injection solution is hypertonic it will cause the water to flow out of the red blood cells and the cells will become shrivel and crenated. If the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane is equal then there is no tendency for water to move across the membrane and no osmotic pressure. Where on the cell are these molecular markers found.
Conversely when animal cells are placed in a hypotonic solution lower concentration of solutes than the cell water moves into the cell and unlike plant or. Reserve the remainder for later experiments. The solutions are isotonic with respect to each other.
Water enters the cell. Since water can flow through the cell membrane cells that experience different tonicities are subject to different effects. Water enters the cell.
- diffusion of water - the solvent water rather than the solute is moving across a selectively permeable membrane. - osmosis is the movement of water across a membrane from the side with more water less solute to the side with less water more solute. Based on the data from this experiment hypothesize which potato has the highest natural carbohydrate concentration.
Cholera kills over 100000 people each year worldwide due to diarrhea. The first will have shrunk after half an hour suggesting that water is diffusing from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated solution. In contrast the one in the tap water solution will inflate somewhat suggesting that it is absorbing water.
Whenever two solutions are separated by a semipermeable membrane that is. Osmotic pressure is defined as the hydrostatic pressure required to stop the flow of water and thus osmotic and hydrostatic pressures are for all intents and purposes equivalent. The cholera toxin opens the CFTR chloride channel in the intestines so that sufferers lose chloride sodium and massive amounts of water.
From that midpoint even a tiny increase or decrease in tonicity resulting from a change in water or sodium balance elicits a prompt change in vasopressin secretion and urine production as well as in thirst and water intake. European Respiratory Journal 1994. The ability of a solution to make water move is called tonicity.
In a hypotonic solution the extracellular fluid has a lower osmolarity than the fluid inside the cell. Similarly if the injection solution is hypotonic it will cause the water to flow into the red blood cells and the cells become swollen and result in hemolysis. Whether the water is trickling out or its just a bit weaker than usual low water pressure can be annoying.
Placing red blood cells in any solution which contains a lesser degree of solute than that of the solution within the cells will cause water to diffuse into. Drugs are administered to the eye for local effects such as miosis mydriasis and anesthesia or to reduce intraocular pressure in treating glaucoma. The resultant increase decrease in body water rapidly restores tonicity to the equilibrium level.
Type of transport that does not require energy to occur. Ophthalmic preparations deliver a drug on the eye into the eye or onto the conjunctiva. Bio 166 chapter 5.
In a hypotonic solution the extracellular fluid has a lower osmolarity than the fluid inside the cell. Water is one of the most complex and amazing materials in the universe. Cut a potato in half and place one half in salt water and the other half in regular water.
Regional deposition of saline aerosols of different tonicities in normal and asthmatic subjects. Fill Beaker 3 with 100 mL of water and submerge the four pieces of dialysis tubing in the water for at least 10 minutes. The result makes a water molecule have a net positive charge near the hydrogen atom.
A solution with a lower concentration of solute has lower osmolarity than one that contains a higher concentration of solute. Water moves from the side of the membrane with lower osmolarity and more water to the side with higher osmolarity and less water. Answer 1 of 10.
Use the permanent marker to label the three 250 mL beakers as 1 2 and 3. Slow water flow can be an indication of several issues. The hydrogen electron orbits all three atoms.
Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package. Water moves from the side of the membrane with lower osmolarity and more water to the side with higher osmolarity and less water. Cells placed in a hypotonic solution will take in water across their membranes until both the external solution and the cytosol are isotonic.
The net movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. The tonicity of a solution is related to its osmolarity which is the total concentration of solute. By knowing the causes of low water pressure and a few simple solutions you can try.
The ability of an extracellular solution to make water move into or out of a cell by osmosis. Tonicity is a bit different from osmolarity because it takes into account both relative solute concentrations and the cell membranes permeability to those solutes. If a cell is in an isotonic environment the solution surrounding the cell has the same osmolarity as the solution within the cell.
There is a higher concetration of solute outsideof the cell and causes a flow of water from inside to outside. The molecules of water are made of two hydrogen and one oxygen and atom. Blood groups such as A B and O are due to glycosylation markers.
Explain how this may influence the water potential of each type of potato.

Tonicity Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Solutions Article Khan Academy

Schematic Diagram Of Tonicity Water Shift And Cellular Volume Arrows Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "I Can Explain How Water Will Flow in Different Tonicities"
Post a Comment